Dewatering Centrifugation is used for both thickening and dewatering of sewage sludge, where dewatered sludge has a higher dry solids (DS) concentration. The centrifuge technologies used for each is almost identical. The key operational differences between the two functions are:
-
the rotation speed employed
-
the throughput, and
-
the nature of the concentrated solids product generated.
Dewatering demands more energy than thickening since more water must be removed to achieve the higher solids concentrations. The dewatered product, whose dry solids (DS) content may be as high as 50%, takes the form of a cake: a deformable semi-solid which forms lumps rather than a free-flowing fluid. It can therefore only be conveyed using a conveyor belt, whereas a thickened product retains the fluid properties of the feed and can be pumped.
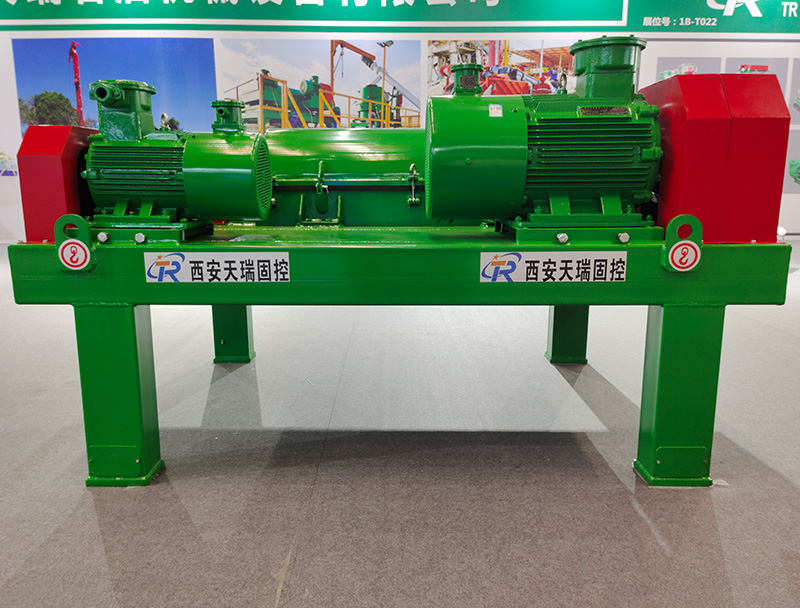
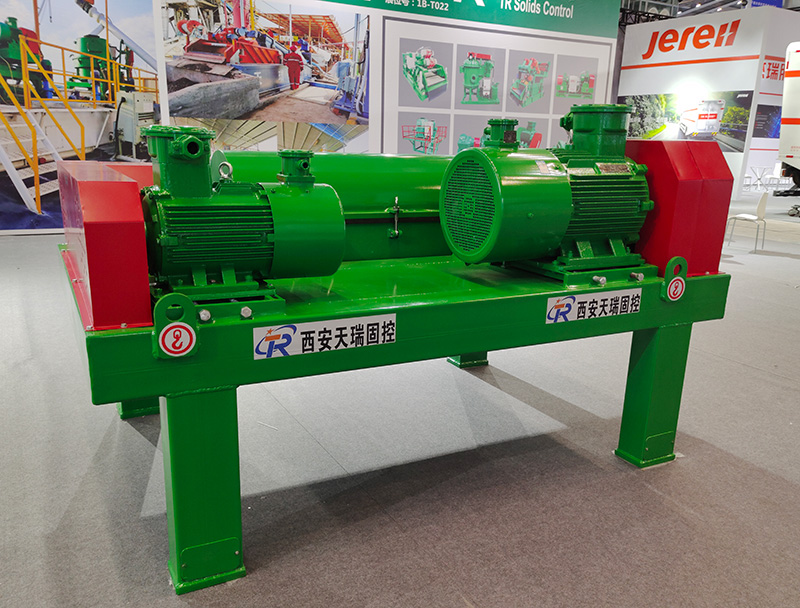
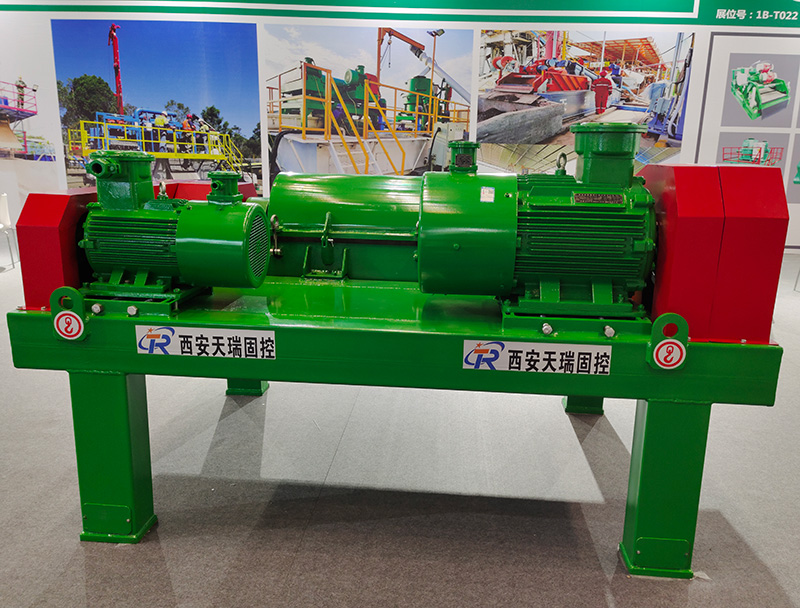
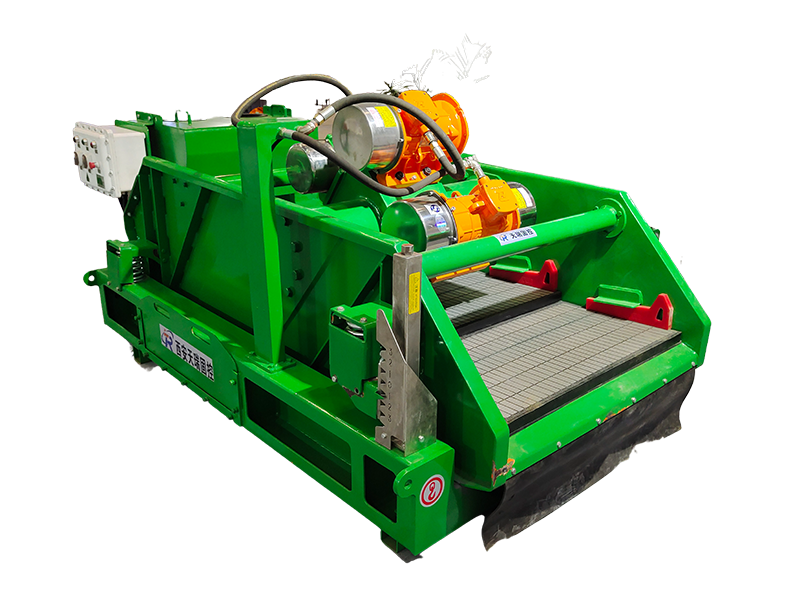
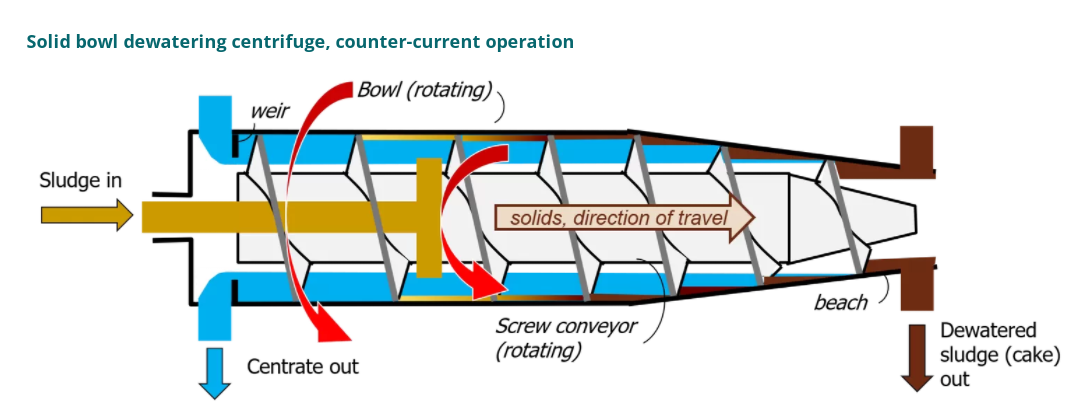
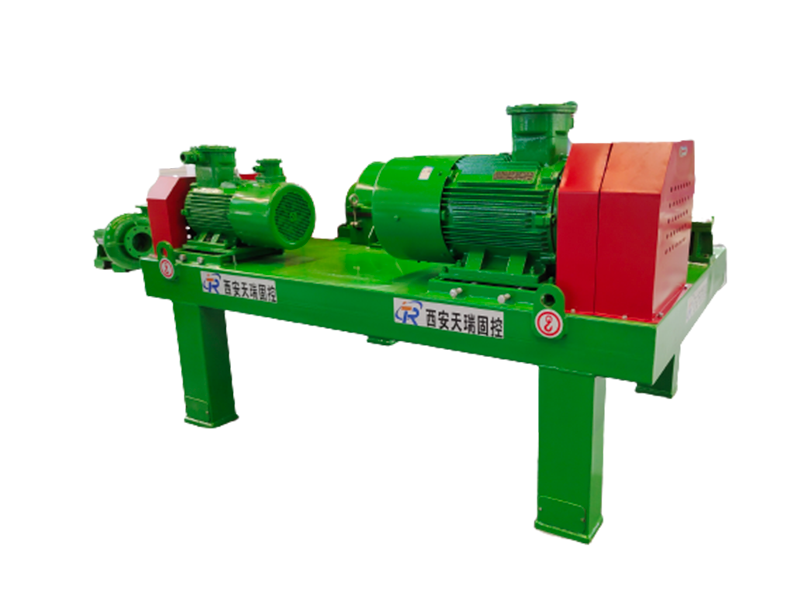
As with thickening, the most common type of centrifuge used for dewatering applications is the solid bowl centrifuge, usually referred to as a decanter or a decanting centrifuge. Its dewatering performance and solids recovery depends on the feed sludge quality and dosing conditions| Model | TRGLW355N-1V | TRGLW450N-2V | TRGLW450N-3V | TRGLW550N-1V |
| Bowl Diameter | 355mm (14inch) | 450mm (17.7inch) | 450mm (17.7inch) | 550mm (22inch) |
| Bowl Length | 1250mm(49.2inch) | 1250mm(49.2inch) | 1600(64inch) | 1800mm(49.2inch) |
| Max Capacity | 40m3/h | 60m3/h | 70m3/h | 90m3/h |
| Max Speed | 3800r/min | 3200r/min | 3200r/min | 3000r/min |
| Rotary Speed | 0~3200r/min | 0~3000r/min | 0~2800r/min | 0~2600r/min |
| G-Force | 3018 | 2578 | 2578 | 2711 |
| Separation | 2~5μm | 2~5μm | 2~5μm | 2~5μm |
| Main Drive | 30kW-4p | 30kW-4p | 45kW-4p | 55kW-4p |
| Back Drive | 7.5kW-4p | 7.5kW-4p | 15kW-4p | 22kW-4p |
| Weight | 2950kg | 3200kg | 4500kg | 5800kg |
| Dimension | 2850X1860X1250 | 2600X1860X1250 | 2950X1860X1250 | 3250X1960X1350 |